AHRS - Attitude and Heading Reference System
The SBC contains code to compute an AHRS solution based entirely on GPS/GNSS RTK signals.
To calculate the attitude of your system, the following conditions must be met:
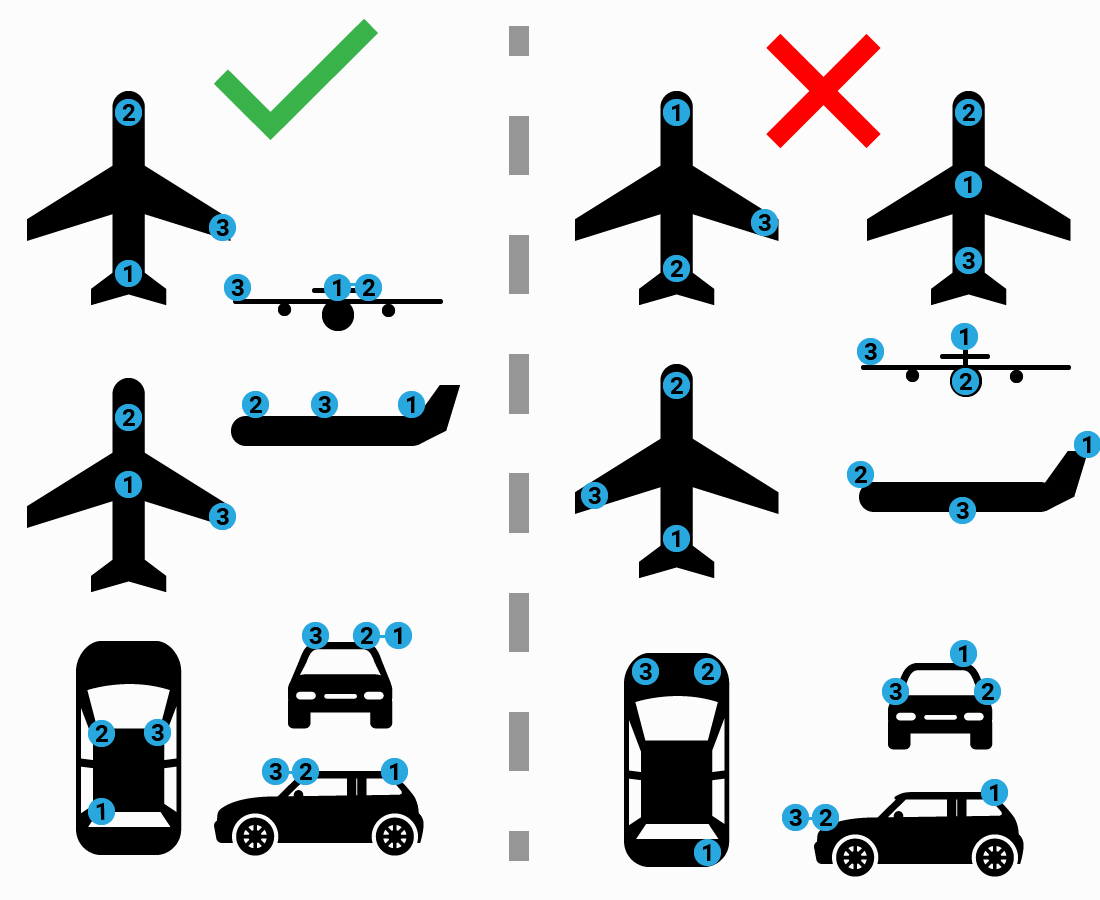
GNSS1 and GNSS2 antennas are placed in the forward direction axis of your vehicle frame
GNSS2 antenna is “in front” of GNSS1 antenna
GNSS3 antenna must be placed to the “right” of the GNSS1-GNSS2 axis
GNSS1, GNSS2 and GNSS3 antennas can’t be aligned
GNSS1, GNSS2 and GNSS3 antennas must be installed at the same height above ground when your frame is leveled
Place the antennas at least 30cm away from each other. The further away the better accuracy you will get.
The detailed distance between antennas is not needed, they can even change their relative position as long as all conditions in this list are met.
The next figures show some valid and not valid installation examples.
Note
To use this class you will need an SBC with 3 GPS/GNSS receivers.
If you need a special configuration for your antenna installation that can’t meet the above conditions, please contact us
Methods
- class CAHRS
The
CAHRSclass contains the attitude of your frame as well as methods to calculate it.- Attributes:
pitch: Your frame pitch angle in [deg]
roll: Your frame roll angle in [deg]
yaw: Your frame yaw (heading) angle in [deg]
q: Your frame quaternion [q0,q1,q2,q3] in frame [e,i,j,k]
v: Axis-angle axis
angle: Axis-angle angle in [rad]
- processInput(receiver1, receiver2)
Compute Euler angles and Quaternions based on the relative position of the 3 GPS/GNSS receivers.
- Args:
receiver1: GNSS2 receiver relative position with respect to GNSS1 receiver in NED reference frame. E.g. [1.5,0.0,0.0]
receiver1: GNSS3 receiver relative position with respect to GNSS1 receiver in NED reference frame. E.g. [0.0,2.3,0.0]- Example to read relative position from 3 GPS/GNSS receivers and calculate frame attitude:
>>> import sbc >>> pm = sbc.Power_Module() >>> parser = sbc.ubx.parser.Parser() >>> ahrs = sbc.CAHRS() >>> pm.gps2and3_on() >>> gps2 = sbc.Gps(2, 38400) >>> gps3 = sbc.Gps(3, 38400) >>> msg = sbc.ubx.request(gps2.get_uart_id(),parser,"NavRelposned") >>> gps2relPos = [msg.relPosN,msg.relPosE,msg.relPosD] >>> print('GNSS2 relative position wrt GNSS1: ',gps2relPos) GNSS2 relative position wrt GNSS1: [1,0,0] >>> msg = sbc.ubx.request(gps3.get_uart_id(),parser,"NavRelposned") >>> gps3relPos = [msg.relPosN,msg.relPosE,msg.relPosD] >>> print('GNSS3 relative position wrt GNSS1: ',gps3relPos) GNSS2 relative position wrt GNSS1: [0,1,0] >>> ahrs.processInput(gps2relPos,gps3relPos) >>> print('Euler angles pitch, roll, yaw: ', ahrs.pitch, ahrs.roll, ahrs.yaw) Euler angles pitch, roll, yaw: 45.0 0.0 0.0 >>> print('Quaternions: ', ahrs.q) Quaternions: [0.9238795, 0.0, 0.3826835, 0.0] >>> print('Axis-angle: ', ahrs.v, ahrs.angle) Axis-angle: [0.0, 1.0, 0.0] 0.7853982